When we think about inheritance one of the important things to learn is overridden methods, in this post I will provide you an overview of this feature of oriented-object, also this post is intented to help you to get all the rules involved to get an OCJP certification.
Let's start with an example
e.g.
If you run this code above you will get:
The MacBook is turned on
The Computer is turned on
The reference variable determines at runtime which method will run depending on instanced object.
Notice that the method openMacOS() cannot be invoked using the reference variable Computer, this variable doesn't know anything about specific methods defined by MacBook class.
Also the overridding method cannot have a more restrictive access modifier, in this case the method turnOn() cannot be private, protected or default.
Let's review the rules.
1. The argument list must be exactly the same as the method that you're overrinding otherwide you're overloading a method.
2. The return type must be the same as, or a subtype of an overridden method declared in a superclass.
3. The access level can't be more restrictive than the overridden method's, but can be less restrictive.
4.
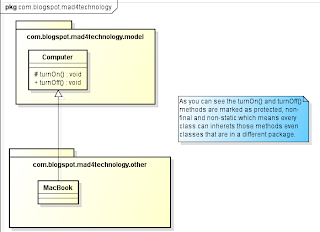
5.
-The overriding method CAN throw any unchecked (runtime) exception
-If the method declared in a superclass throws a checked exception the overriding method must throw a checked exceptions that match in a test IS-A.
6. Look at the modifiers: method marked as final or static cannot be overriden.
7. Methods that cannot be inherited cannot be overriden, so watch out the access modifiers.
Invoking a Superclass Version
We can invoke the superclass method by using super.methodName().
No comments:
Post a Comment